For those of you that are unfamiliar with the HITME project, it is a set of deployed HoneyPoints that gather real-world, real-time attacker data from around the world. The sensors gather attack sources, frequency, targeting information, vulnerability patterns, exploits, malware and other crucial event data for the technical team at MSI to analyze. We frequently feed these attack signatures into our vulnerability management service to ensure that our customers are tested against the most current forms of attacks being used on the Internet.
On a monthly basis, we have been taking a step back and looking at our HITME data from a bird’s eye view to find common attack patterns. Throughout December, we observed a significant increase in attacks against Port 123 (NTP). This is due to the recent discovery of a vulnerability within NTP.
A majority of the attacks we observed against Port 123 appeared to originate out of the United States of America, Germany, Switzerland, Russia, and China.
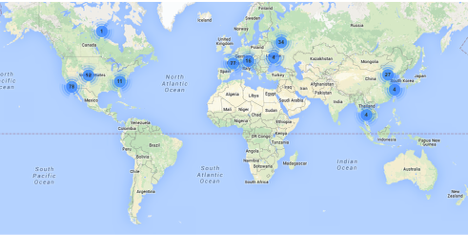
This vulnerability should be addressed as soon as possible as exploits are publicly available. All NTP Version 4 releases prior to Version 4.2.8 are vulnerable and need to be updated to Version 4.2.8. Do not hesitate to contact us at info@microsolved.com if you require any assistance in responding to this vulnerability.
This blog post by Adam Luck.
