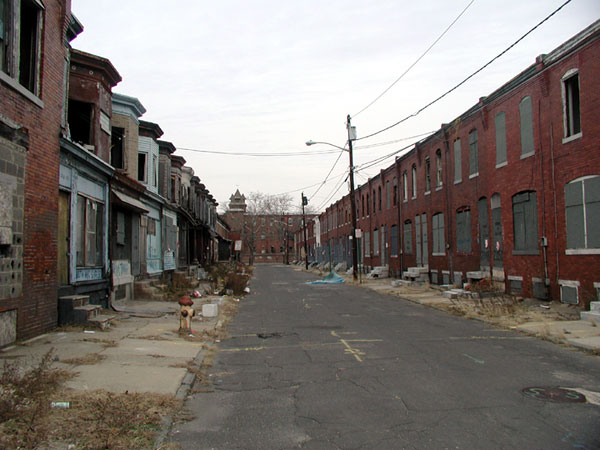
If, when you wake up in the morning, you look out outside and view something like the image below, you probably understand that you are not in the best of all possible worlds.
So, what “neighborhood” does your website see when it “wakes up”?
It could be just as disquieting.
It is not uncommon for MSI to do an an analysis of the Internet services offered by an organization and find that those services are being delivered from a “shared service” environment.
The nature of those shared services can vary.
VM Hosting:
Often they are simply the services of an virtual machine hosting provider such as Amazon AWS. Sometimes we find the entire computing infrastructure of a customer within such an environment.
The IP addressing is all private – the actual location is all “cloud”.
The provider in this case is running a “hypervisor” on it’s own hardware to host the many virtual machines used by its clients.
Application Hosting:
Another common occurrence is to find third-party “under the covers” core application services being linked to from a customer’s website. An example of such a service is that provided by commercial providers of mortgage loan origination software to much of the mortgage industry.
For example, see: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ellie_Mae
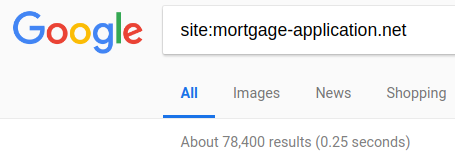
A quick google of “site:mortgage-application.net” will give you an idea of the extent to which the service is used by mortgage companies. The landing sites are branded to the customer, but they are all using common shared infrastructure and applications.
Web Site hosting:
Most often the shared service is simply that provided by a website hosting company. Typically many unique websites are hosted by such companies. Although each website will have a unique name (e.g. mywebsite.com) the underlying infrastructure is common. Often many websites will share a common IP address.
It is in this particular “shared service” space we most often see potential issues.
Often it’s simply a reputation concern. For instance:
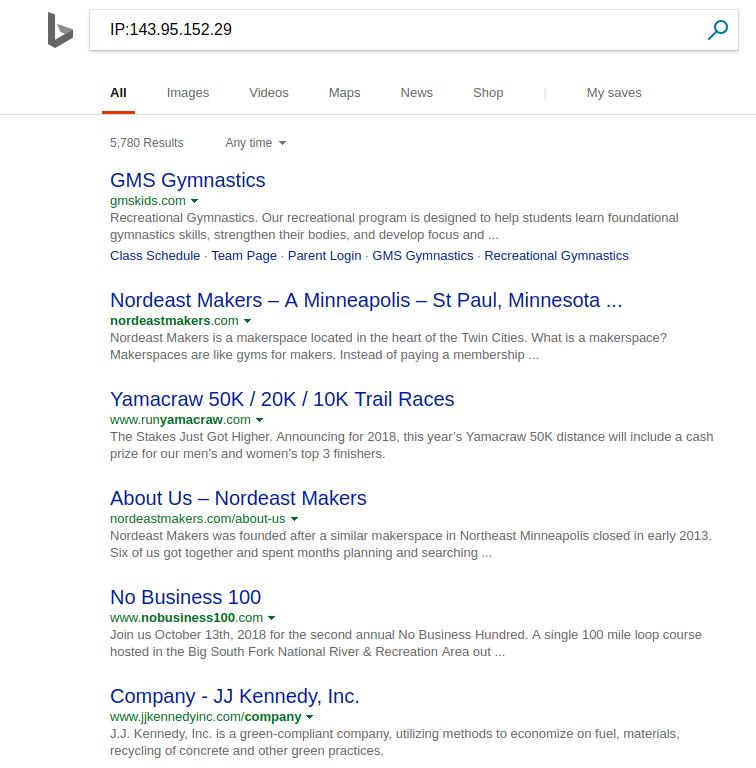
host www.iwantporn.net
www.iwantporn.net is an alias for iwantporn.net.
iwantporn.net has address 143.95.152.29
These are some of the sites that are (or have recently been) on that same IP address according to Microsoft’s Bing search engine:
My guess I some of the website owners would be uncomfortable knowing they are being hosted via the same IP address and same infrastructure as is www.iwantporn.com.
They might also be concerned about this:
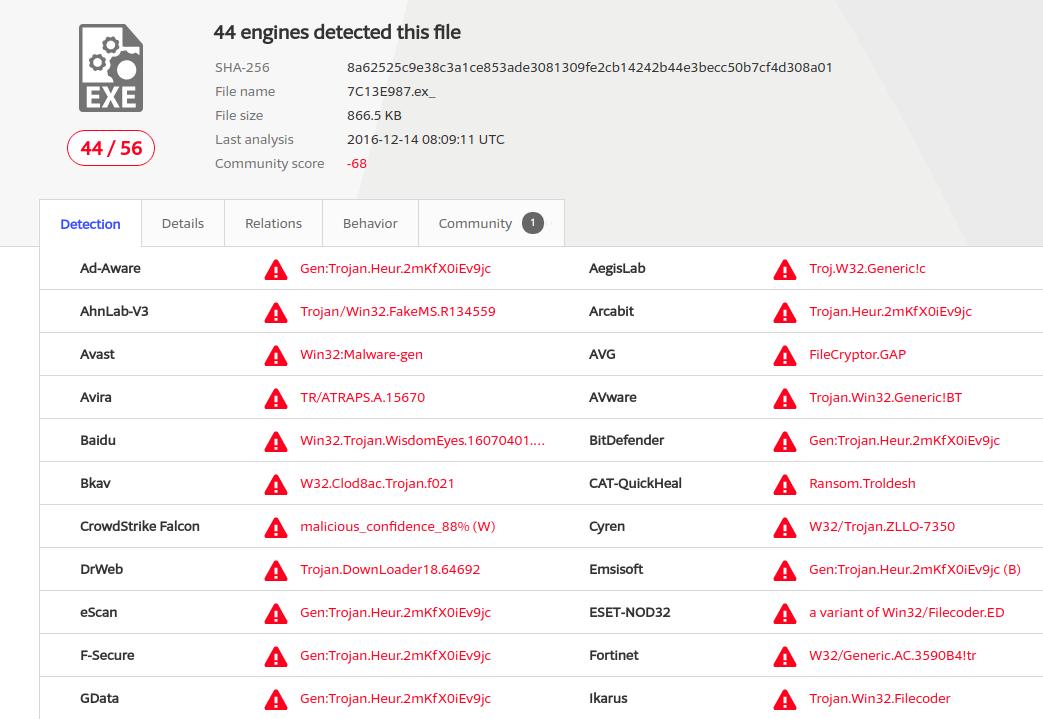
https://www.virustotal.com/#/ip-address/143.95.152.29
Virustotal is reporting that a known malicious program was seen communicating with a listening service running on some site with the IP address 143.95.152.29 .
The implication is that some site hosted at 143.95.152.29 had in the past been compromised and was being used for communications in what may have been a ransomware attack.
The IP address associated with such a compromised system can ultimately be blacklisted as a known suspicious site,
All websites hosted on the IP address can be affected.
Website traffic and the delivery of emails can all be affected as a result of the misfortune to share an IP address with a suspect site.
“Backplaning”
When such a compromise of the information space used by a client in a shared service occurs, all other users of that service can be at risk. Although the initial compromise may simply be the result of misuse of the website owner’s credentials (e.g. stolen login/password), the hosting provider needs to ensure that such a compromise of one site does not allow the attacker to compromise other websites hosted in the same environment – an attack pattern sometimes referred to as backplaning.
The term comes from electronics and refers to a common piece of electronics circuity (e.g a motherboard, an IO bus, etc. ) that separate “plugin” components use to access shared infrastructure.
See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Backplane
Example:
The idea is that a compromised environment becomes the doorway into the “backplane” of underlying shared services. (e.g. possibly shared database infrastructure).
If the provider has not taken adequate precautions such an attack can affect all hosted websites using the shared service.
Such things really can happen.
In 2015 a vulnerability in commonly used hypervisor software was announced. See: http://venom.crowdstrike.com/
An attacker who had already gained administrative rights on a hosted virtual machine could directly attack the hypervisor and – by extension – all other virtual machines hosted in the same environment. Maybe yours?
What to do?
Be aware of your hosted environment’s neighborhood. Use the techniques described above to find out who else is being hosted by your provider. If the neighborhood looks bad, consider a dedicated IP address to help isolate you from the poor administrative practices of other hosted sites.
Contact your vendor to and find out what steps they have in place to protect you from “backplane” attacks and what contractual protections you have if such an attack occurs.
Questions? info@microsolved.com