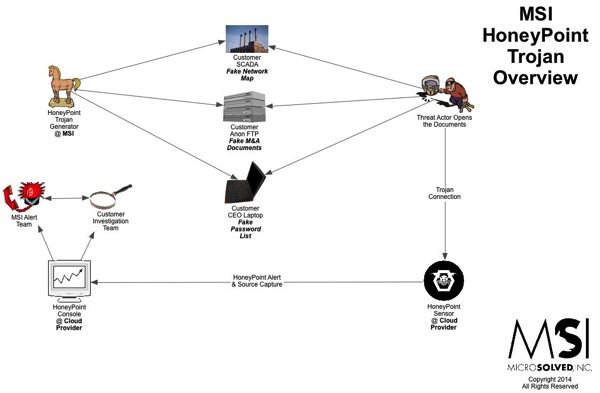
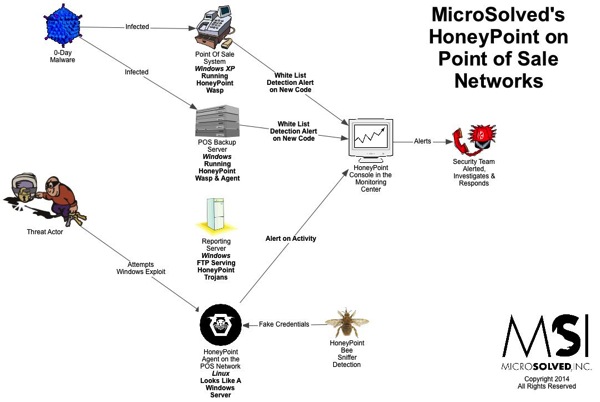
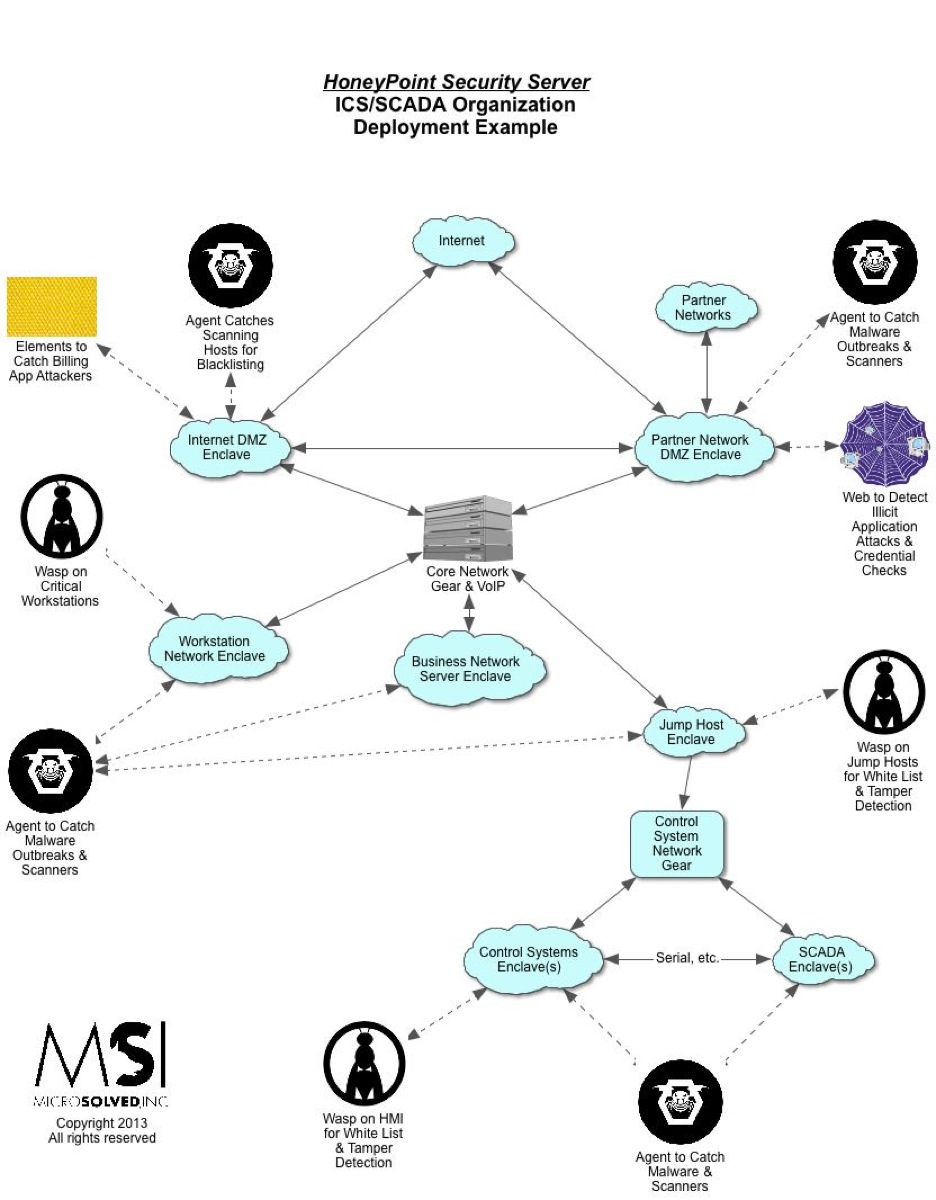
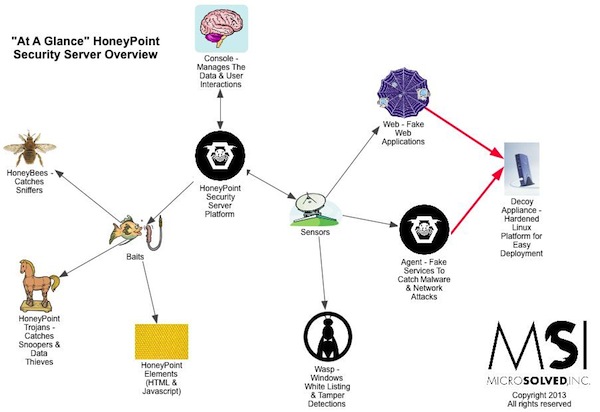
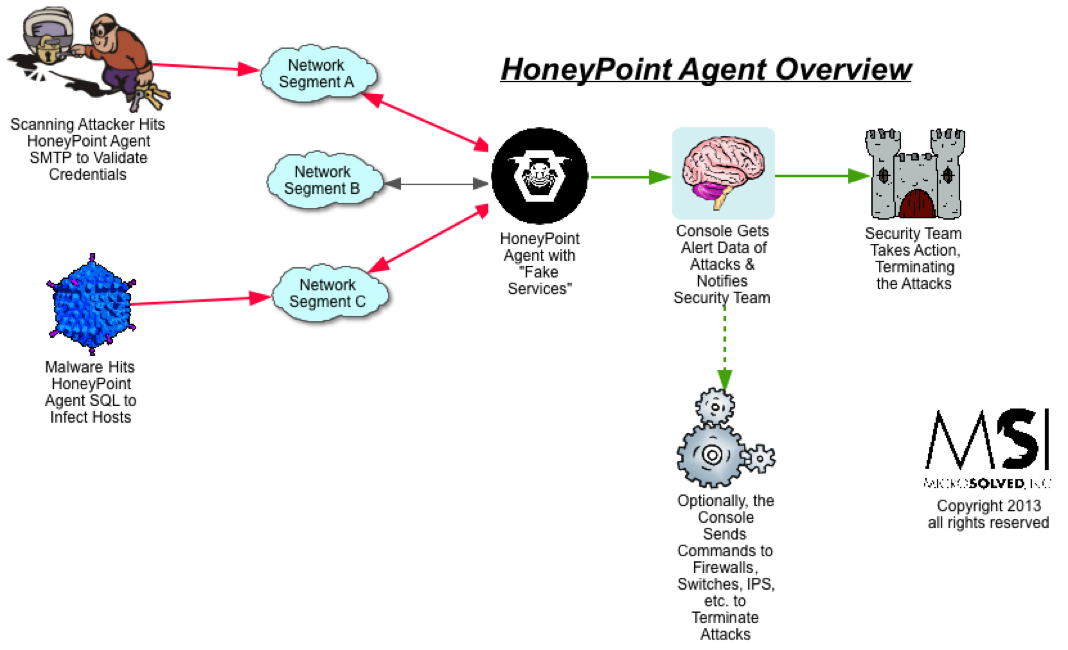
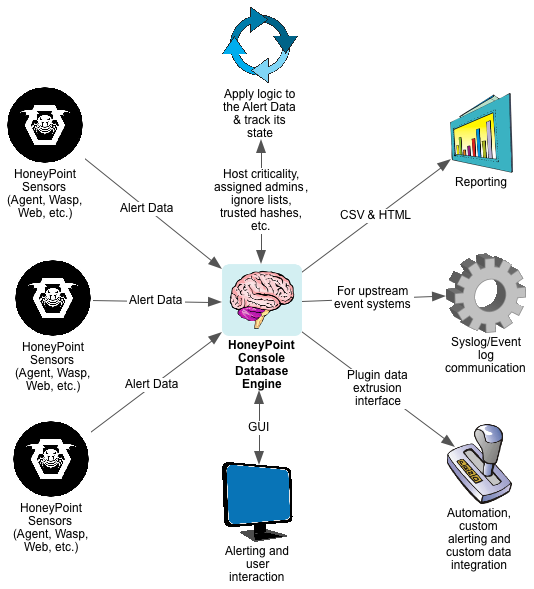
For quite some time now, we have been using HoneyPoint Agent and Console to do some passive inventory and mapping exercises for clients, particularly those involved in ICS and SCADA deployments where active scanning to get inventories is often strongly discouraged. We had particular success with a specific client in this space a couple of weeks ago, and I wanted to discuss it here, since it has proven itself to be a useful tool and is on the top of my mind at the moment.
To get an inventory of the Windows systems on a collision domain, you simply install the Agent on a Linux box (or I suggest using the virtual appliance we already have built for your ease) and implement it and the Console. Once HoneyPoint is operational, you configure a UDP listener on port 138. From there, all of the NETBios speaking Windows systems will begin to send traffic to the host, as per the usual behavior of those systems. In this case, however, HoneyPoint will capture each source IP and log it to the Console. It will also capture the UDP datagrams from that conversation and place them as event data in the logs. By reviewing the source IPs, you can quickly and easily take stock of the Windows systems on the collision domain without sending any traffic at all to the systems. As a bonus, if you dig into the datagram data, you will also see the names of the hosts and other information.
Most of the time, this technique captures only Windows boxes, but if you have other devices out there running NETBios, they will likely get detected as well. This can include embedded systems, Unix systems running SAMBA, printers and copiers, Windows CE systems (often seen in many field equipment deployments), etc. You might be surprised what you can find.
Try this with a laptop, and move the laptop around your environment. You can pretty quickly and easily get an inventory by collision domain. You can also try dialing other NETBios ports and see if you get traffic that is routed across your switching fabric. Depending on your configuration, you might be able to gather a great deal of inventory data from a single location (especially if your network is flat and switches are poorly configured).
Give this a shot or get in touch if you would like us to come onsite and perform the inventory for you. We think it is a pretty useful technique and one that many folks are enjoying the benefits of. Let us know what you think when you give it a run in your network!
As always, thanks for reading, and until next time, stay safe out there!
PS – You can also do this with HoneyPoint Personal Edition on a Linux system, which makes it very easy and cheap to do if you don’t want to invest in a full blown HoneyPoint Security Server implementation. (You should invest though, it is a FANTASTIC detection tool!)
**(The link above is for HPPE on Windows, but if you purchase a license and contact us, we will send you the Linux build right away. You can’t easily capture port 138/UDP traffic in Windows HPPE because Windows has those ports in use…)