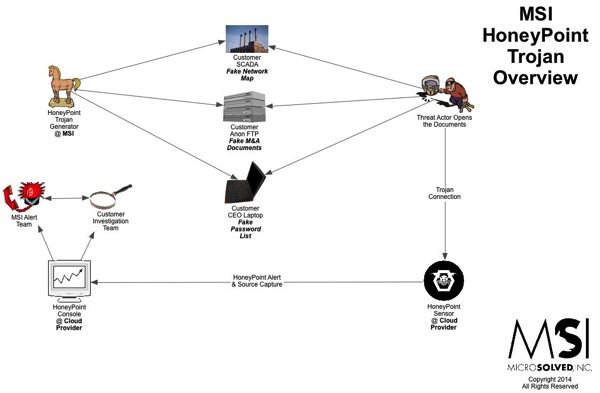
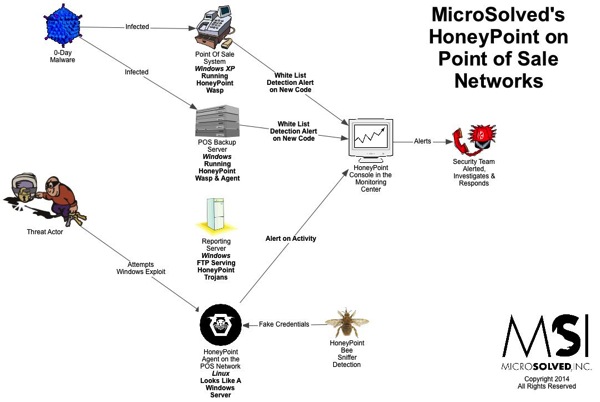
I found this article quite interesting, as it gives you a heads up about the state of endpoint security, at least according to Ponemon. For those who want to skim, here is a quick summary:
“Maintaining endpoint security is tougher than ever, security professionals say, thanks largely to the huge influx of mobile devices.
According to the annual State of the Endpoint study, conducted by the Ponemon Institute and sponsored by Lumension, 71 percent of security professionals believe that endpoint security threats have become more difficult to stop or mitigate over the past two years.
…More than 75 percent said mobile devices pose the biggest threat in 2014, up from just 9 percent in 2010, according to Ponemon. Some 68 percent say their mobile devices have been targeted by malware in the past 12 months, yet 46 percent of respondents say they do not manage employee-owned mobile devices.
…And unfortunately, 46 percent of our respondents report no efforts are in place to secure them.”
…While 40 percent report they were a victim of a targeted attack in the past year, another 25 percent say they aren’t sure if they have been, which suggests that many organizations don’t have security mechanisms in place to detect such an attack, the study says. For those that have experienced such an attack, spear-phishing emails sent to employees were identified as the No. 1 attack entry point.
…The survey found that 41 percent say they experience more than 50 malware attacks a month, up 15 percent from those that reported that amount three years ago. And malware attacks are costly, with 50 percent saying their operating expenses are increasing and 67 percent saying malware attacks significantly contributed to that rising expense.
…While 65 percent say they prioritize endpoint security, just 29 percent say their budgets have increased in the past 24 months.” — Dark Reading
There are a couple of things I take away from this:
- Organizations are still struggling with secure architectures and enclaving, and since that is true, BYOD and visiblility/prevention efforts on end-points are a growing area of frustration.
- Organizations that focus on secure architectures and enclaving will have quicker wins
- Organizations with the ability to do nuance detection for enclaved systems will have quicker wins
- Organizations are still focusing on prevention as a primary control, many of them are seriously neglecting detection and response as control families
- Organizations that embrace a balance of prevention/detection/response control families will have quicker wins
- Organizations are still struggling in communicating to management and the user population why end-point security is critical to long term success
- Many organizations continue to struggle with creating marketing-based messaging for socialization of their security mission
If you would like to discuss some or all of these ideas, feel free to ping me on Twitter (@lbhuston) or drop me an email. MSI is working with a variety of companies on solutions to these problems and we can certainly share what we have learned with your organization as well.