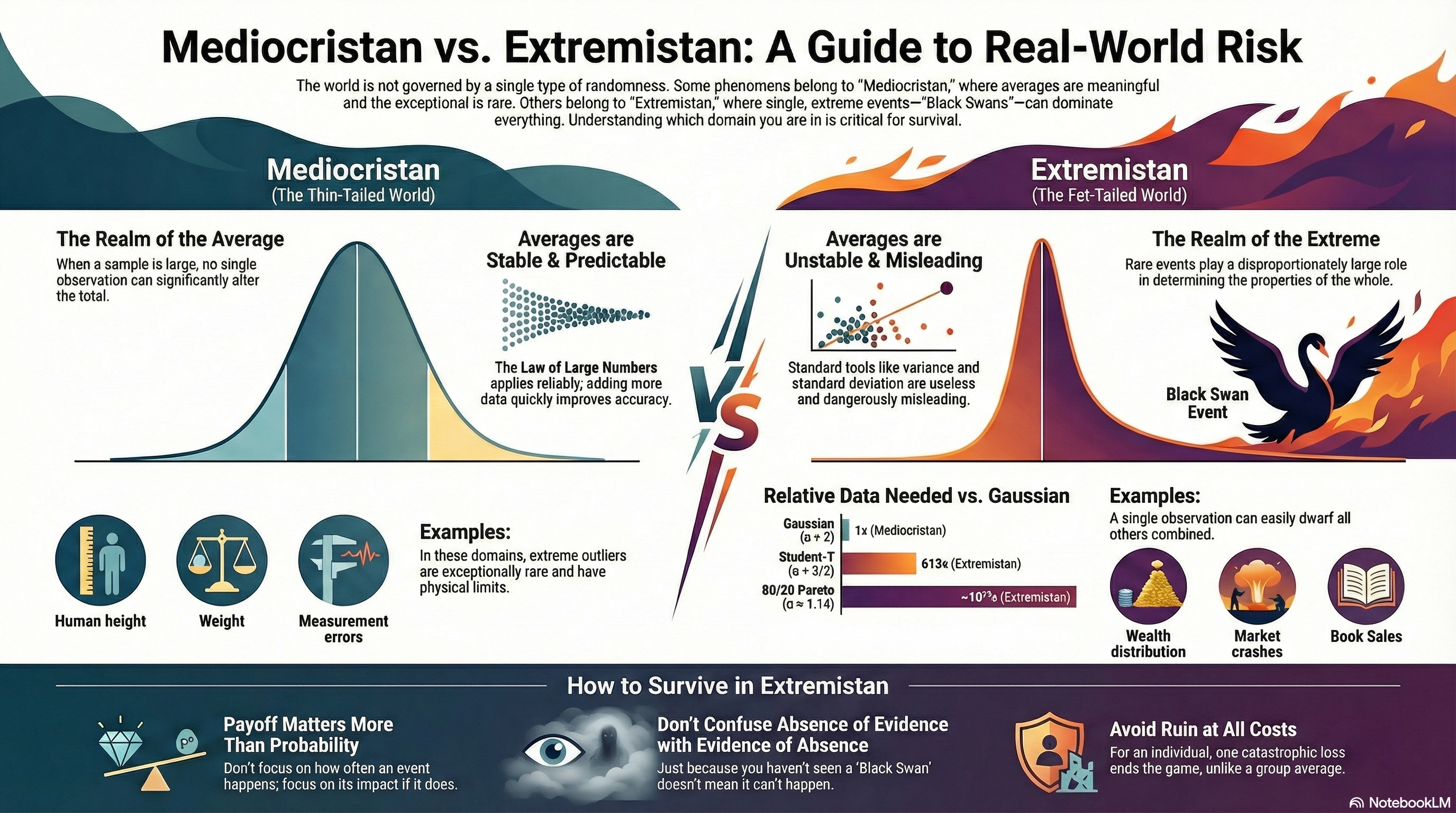
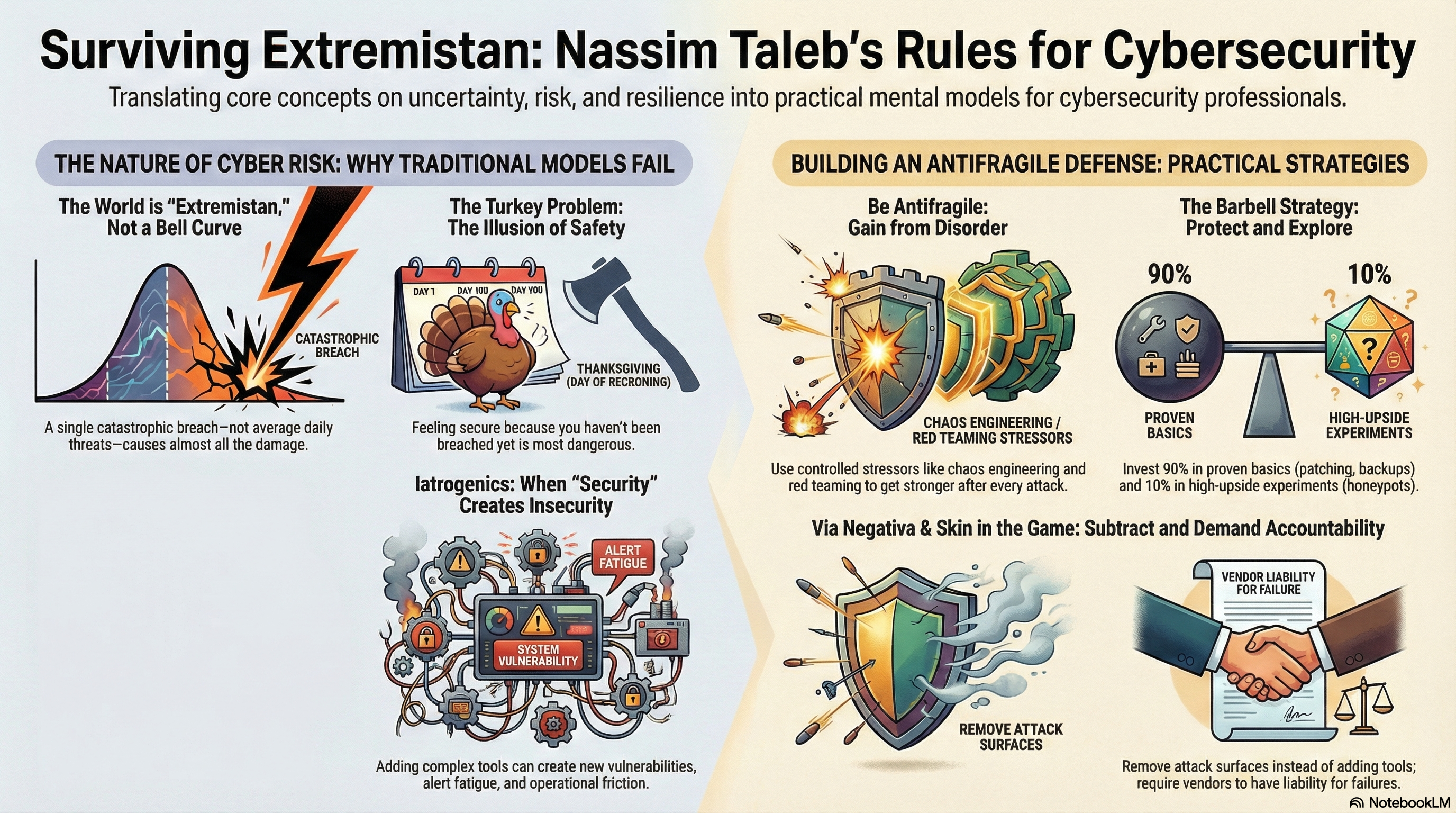
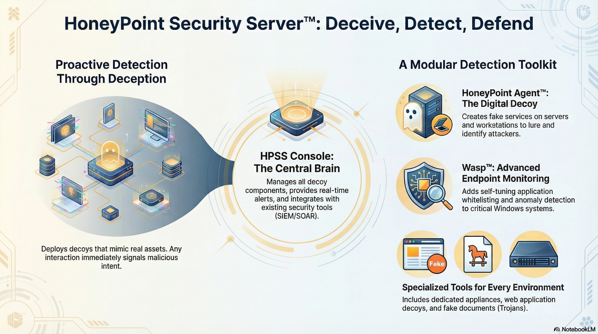
The Impetus: Wanting Something We Could Actually Run
Like many security folks watching the rise of LLM-driven workflows, I kept hearing the same conversations about prompt injection. They were thoughtful discussions. Smart people. Solid theory.
But the theory wasn’t what I wanted.
What I wanted was something we could actually run.
The moment that really pushed me forward came when I started testing real prompt-injection payloads against simple LLM workflows that pull content from the internet. Suddenly, the problem didn’t feel abstract anymore. A malicious instruction buried in retrieved text could quietly override system instructions, leak data, or coerce tools.
At that point, the goal became clear: build a practical defensive layer that could sit between untrusted content and an LLM — and make sure the application didn’t fall apart when something suspicious showed up.

What I Set Out to Build
The initial concept was simple: create a defensive scanner that could inspect incoming text before it ever reached a model. That idea eventually became PromptShield.
PromptShield focuses on defensive controls:
-
Scanning untrusted text and structured data
-
Detecting prompt injection patterns
-
Applying context-aware policies based on source trust
-
Routing suspicious content safely without crashing workflows
But I quickly realized something important:
Security teams don’t just need blocking.
They need proof.
That realization led to the second tool in the suite: InjectionProbe — an offensive assessment library and CLI designed to test scripts and APIs with standardized prompt-injection payloads and produce structured reports.
The goal became a full lifecycle toolkit:
-
PromptShield – Prevent prompt injection and sanitize risky inputs
-
InjectionProbe – Prove whether attacks still succeed
In other words: one suite that both blocks attacks and verifies what still slips through.
The Build Journey
Like many engineering projects, the first version was far from elegant. It started with basic pattern matching and policy routing.
From there, the system evolved quickly:
-
Structured payload scanning
-
JSON logging and telemetry
-
Regression testing harnesses
-
Red-team simulation frameworks
Over time the detection logic expanded to handle a wide range of adversarial techniques including:
-
Direct prompt override attempts
-
Data exfiltration instructions
-
Tool abuse and role hijacking
-
Base64 and encoded payloads
-
Leetspeak and Unicode confusables
-
Typoglycemia attacks
-
Indirect retrieval injection
-
Transcript and role spoofing
-
Many-shot role chain manipulation
-
Multimodal instruction cues
-
Bidi control character tricks
Each time a bypass appeared, it became part of a versioned adversarial corpus used for regression testing.
That was a turning point: attacks became test cases, and the system started behaving more like a traditional secure software project with CI gates and measurable thresholds.
The Fun Part
The most satisfying moments were watching the “misses” shrink after each defensive iteration.
There’s something deeply rewarding about seeing a payload that slipped through last week suddenly fail detection tests because you tightened a rule or added a new heuristic.
Another surprisingly enjoyable part was the naming process.
What started as a set of ad-hoc scripts slowly evolved into something that looked like a real platform. Eventually the pieces came together under a single identity: the MSI PromptDefense Suite.
That naming step might seem cosmetic, but it matters. Branding and workflow clarity are often what turn a security experiment into something teams actually adopt.
Lessons Learned
A few practical lessons emerged during the process:
-
Defense and offense must evolve together. Building detection without testing is guesswork.
-
Fail-safe behavior matters. Detection should never crash the application path.
-
Attack corpora should be versioned like code. This prevents security regressions.
-
Context-aware policy is a major win. Not all sources deserve the same trust level.
-
Clear reporting drives adoption. Security tools need outputs stakeholders can understand.
One practical takeaway: prompt injection testing should look more like unit testing than traditional penetration testing. It should be continuous, automated, and measurable.
Where Things Landed
The final result is a fully operational toolkit:
-
PromptShield defensive scanning library
-
InjectionProbe offensive testing framework
-
CI-style regression gates
-
JSON and Markdown assessment reporting
The suite produces artifacts such as:
-
injectionprobe_results.json -
injectionprobe_findings_todo.md -
assessment_report.json -
assessment_report.md
These outputs give both developers and security teams a consistent way to evaluate the safety posture of AI-integrated systems.
What Comes Next
There’s still plenty of room to expand the platform:
-
Semantic classifiers layered on top of pattern detection
-
Adapters for queues, webhooks, and agent frameworks
-
Automated baseline policy profiles
-
Expanded adversarial benchmark corpora
The AI ecosystem is evolving quickly, and defensive tooling needs to evolve just as fast.
The good news is that the engineering model works: treat attacks like test cases, keep the corpus versioned, and measure improvements continuously.
More Information and Help
If your organization is integrating LLMs with internet content, APIs, or automated workflows, prompt injection risk needs to be part of your threat model.
At MicroSolved, we work with organizations to:
-
Assess AI-enabled systems for prompt injection risks
-
Build practical defensive guardrails around LLM workflows
-
Perform offensive testing against AI integrations and agent systems
-
Implement monitoring and policy enforcement for production environments
If you’d like to explore how tools like the MSI PromptDefense Suite could be applied in your environment — or if you want experienced consultants to help evaluate the security of your AI deployments — contact the MicroSolved team to start the conversation.
Practical AI security starts with testing, measurement, and iterative defense.
* AI tools were used as a research assistant for this content, but human moderation and writing are also included. The included images are AI-generated.