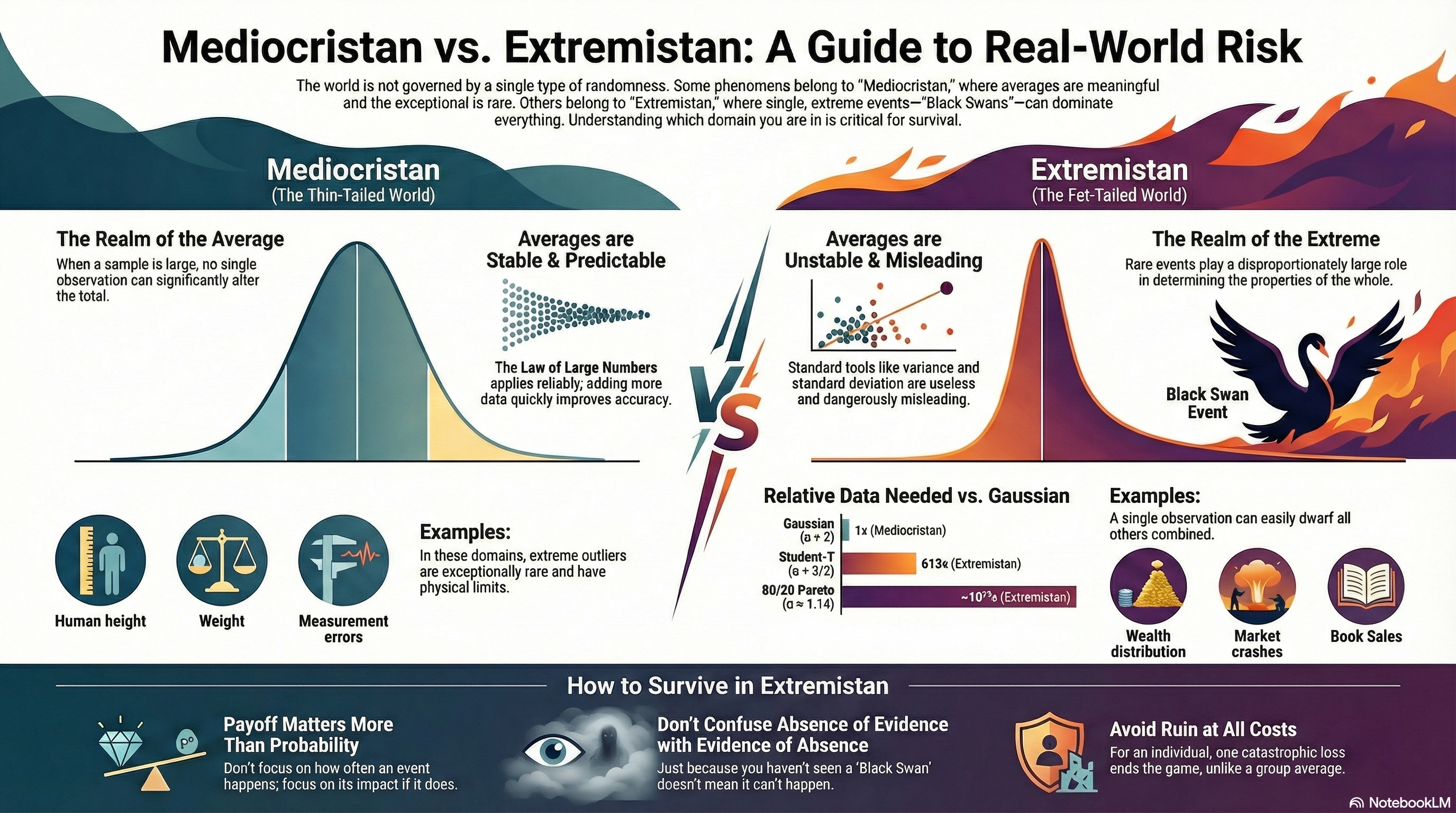
Six months after a major alert-reduction initiative, a SOC director proudly reports a 42% decrease in daily alerts. The dashboards look cleaner. The queue is shorter. Analysts are no longer drowning.
Leadership applauds the efficiency gains.
Then reality intervenes.
A lateral movement campaign goes undetected for weeks. Analyst burnout hasn’t meaningfully declined. The cost per incident response remains stubbornly flat. And when the board asks a simple question — “Are we more secure now?” — the answer becomes uncomfortable.
Because while alert volume decreased, risk exposure may not have.
This is the uncomfortable truth: alert volume is a throughput metric. It tells you how much work flows through the system. It does not tell you how much value the system produces.
If we want to mature security operations beyond operational tuning, we need to move from counting alerts to measuring signal yield. And to do that, we need to treat detection engineering not as a technical discipline — but as an economic system.

The Core Problem: Alert Volume Is a Misleading Metric
At its core, an alert is three things:
-
A probabilistic signal.
-
A consumption of analyst time.
-
A capital allocation decision.
Every alert consumes finite investigative capacity. That capacity is a constrained resource. When you generate an alert, you are implicitly allocating analyst capital to investigate it.
And yet, most SOCs measure success by reducing the number of alerts generated.
The second-order consequence? You optimize for less work, not more value.
When organizations focus on alert reduction alone, they may unintentionally optimize for:
-
Lower detection sensitivity
-
Reduced telemetry coverage
-
Suppressed edge-case detection
-
Hidden risk accumulation
Alert reduction is not inherently wrong. But it exists on a tradeoff curve. Lower volume can mean higher efficiency — or it can mean blind spots.
The mistake is treating volume reduction as an unqualified win.
If alerts are investments of investigative time, then the right question isn’t “How many alerts do we have?”
It’s:
What is the return on investigative time (ROIT)?
That is the shift from operations to economics.
Introducing Signal Yield: A Pareto Model of Detection Value
In most mature SOCs, alert value follows a Pareto distribution.
-
Roughly 20% of alert types generate 80% of confirmed incidents.
-
A small subset of detections produce nearly all high-severity findings.
-
Entire alert families generate near-zero confirmed outcomes.
Yet we often treat every alert as operationally equivalent.
They are not.
To move forward, we introduce a new measurement model: Signal Yield.
1. Signal Yield Rate (SYR)
SYR = Confirmed Incidents / Total Alerts (per detection family)
This measures the percentage of alerts that produce validated findings.
A detection with a 12% SYR is fundamentally different from one with 0.3%.
2. High-Severity Yield
Critical incidents / Alert type
This isolates which detection logic produces material risk reduction — not just activity.
3. Signal-to-Time Ratio
Confirmed impact per analyst hour consumed.
This reframes alerts in terms of labor economics.
4. Marginal Yield
Additional confirmed incidents per incremental alert volume.
This helps determine where the yield curve flattens.
The Signal Yield Curve
Imagine a curve:
-
X-axis: Alert volume
-
Y-axis: Confirmed incident value
At first, as coverage expands, yield increases sharply. Then it begins to flatten. Eventually, additional alerts add minimal incremental value.
Most SOCs operate blindly on this curve.
Signal yield modeling reveals where that flattening begins — and where engineering effort should be concentrated.
This is not theoretical. It is portfolio optimization.
The Economic Layer: Cost Per Confirmed Incident
Operational metrics tell you activity.
Economic metrics tell you efficiency.
Consider:
Cost per Validated Incident (CVI)
Total SOC operating cost / Confirmed incidents
This introduces a critical reframing: security operations produce validated outcomes.
But CVI alone is incomplete. Not all incidents are equal.
So we introduce:
Weighted CVI
Total SOC operating cost / Severity-weighted incidents
Now the system reflects actual risk reduction.
At this point, detection engineering becomes capital allocation.
Each detection family resembles a financial asset:
-
Some generate consistent high returns.
-
Some generate noise.
-
Some consume disproportionate capital for negligible yield.
If a detection consumes 30% of investigative time but produces 2% of validated findings, it is an underperforming asset.
Yet many SOCs retain such detections indefinitely.
Not because they produce value — but because no one measures them economically.
The Detection Portfolio Matrix
To operationalize this, we introduce a 2×2 model:
| High Yield | Low Yield | |
|---|---|---|
| High Volume | Core Assets | Noise Risk |
| Low Volume | Precision Signals | Monitoring Candidates |
Core Assets
High-volume, high-yield detections. These are foundational. Optimize, maintain, and defend them.
Noise Risk
High-volume, low-yield detections. These are capital drains. Redesign or retire.
Precision Signals
Low-volume, high-yield detections. These are strategic. Stress test for blind spots and ensure telemetry quality.
Monitoring Candidates
Low-volume, low-yield. Watch for drift or evolving relevance.
This model forces discipline.
Before building a new detection, ask:
-
What detection cluster does this belong to?
-
What is its expected yield?
-
What is its expected investigation cost?
-
What is its marginal ROI?
Detection engineering becomes intentional investment, not reactive expansion.
Implementation: Transitioning from Volume to Yield
This transformation does not require new tooling. It requires new categorization and measurement discipline.
Step 1 – Categorize Detection Families
Group alerts by logical family (identity misuse, endpoint anomaly, privilege escalation, etc.). Avoid measuring at individual rule granularity — measure at strategic clusters.
Step 2 – Attach Investigation Cost
Estimate average analyst time per alert category. Even approximations create clarity.
Time is the true currency of the SOC.
Step 3 – Calculate Yield
For each family:
-
Signal Yield Rate
-
Severity-weighted yield
-
Time-adjusted yield
Step 4 – Plot the Yield Curve
Identify:
-
Where volume produces diminishing returns
-
Which families dominate investigative capacity
-
Where engineering effort should concentrate
Step 5 – Reallocate Engineering Investment
Focus on:
-
Improving high-impact detections
-
Eliminating flat-return clusters
-
Re-tuning threshold-heavy anomaly models
-
Investing in telemetry that increases high-yield signal density
This is not about eliminating alerts.
It is about increasing return per alert.
A Real-World Application Example
Consider a SOC performing yield analysis.
They discover:
-
Credential misuse detection: 18% yield
-
Endpoint anomaly detection: 0.4% yield
-
Endpoint anomaly consumes 40% of analyst time
Under a volume-centric model, anomaly detection appears productive because it generates activity.
Under a yield model, it is a capital drain.
The decision:
-
Re-engineer anomaly thresholds
-
Improve identity telemetry depth
-
Increase focus on high-yield credential signals
Six months later:
-
Confirmed incident discovery increases
-
Analyst workload becomes strategically focused
-
Weighted CVI decreases
-
Burnout declines
The SOC didn’t reduce alerts blindly.
It increased signal density.
Third-Order Consequences
When SOCs optimize for signal yield instead of alert volume, several systemic changes occur:
-
Board reporting becomes defensible.
You can quantify risk reduction efficiency. -
Budget conversations mature.
Funding becomes tied to economic return, not fear narratives. -
“Alert theater” declines.
Activity is no longer mistaken for effectiveness. -
Detection quality compounds.
Engineering effort concentrates where marginal ROI is highest.
Over time, this shifts the SOC from reactive operations to disciplined capital allocation.
Security becomes measurable in economic terms.
And that changes everything.
The Larger Shift
We are entering an era where AI will dramatically expand alert generation capacity. Detection logic will become cheaper to create. Telemetry will grow.
If we continue to measure success by volume reduction alone, we will drown more efficiently.
Signal yield is the architectural evolution.
It creates a common language between:
-
SOC leaders
-
CISOs
-
Finance
-
Boards
And it elevates detection engineering from operational tuning to strategic asset management.
Alert reduction was Phase One.
Signal economics is Phase Two.
The SOC of the future will not be measured by how quiet it is.
It will be measured by how much validated risk reduction it produces per unit of capital consumed.
That is the metric that survives scrutiny.
And it is the metric worth building toward.
* AI tools were used as a research assistant for this content, but human moderation and writing are also included. The included images are AI-generated.