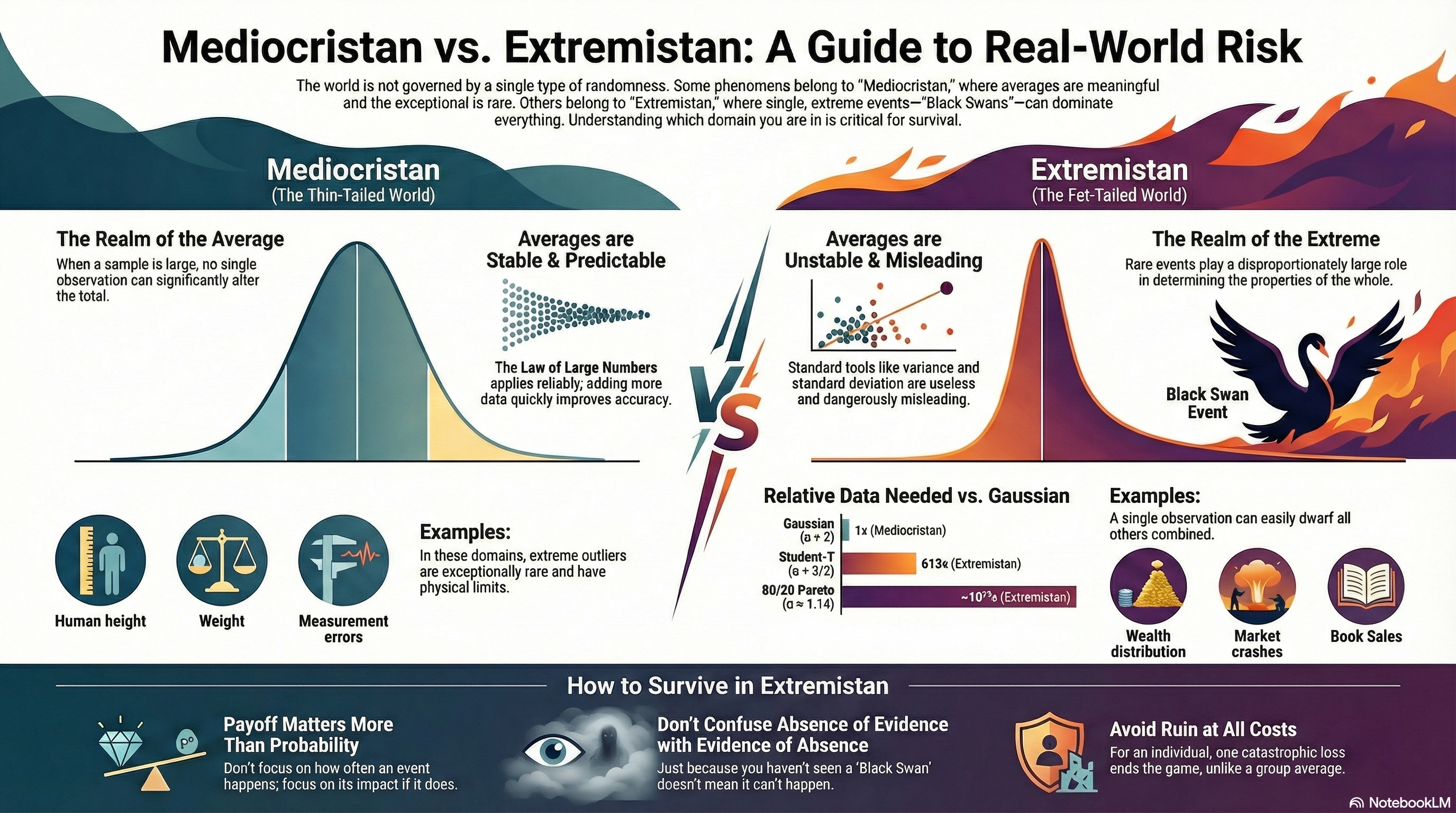
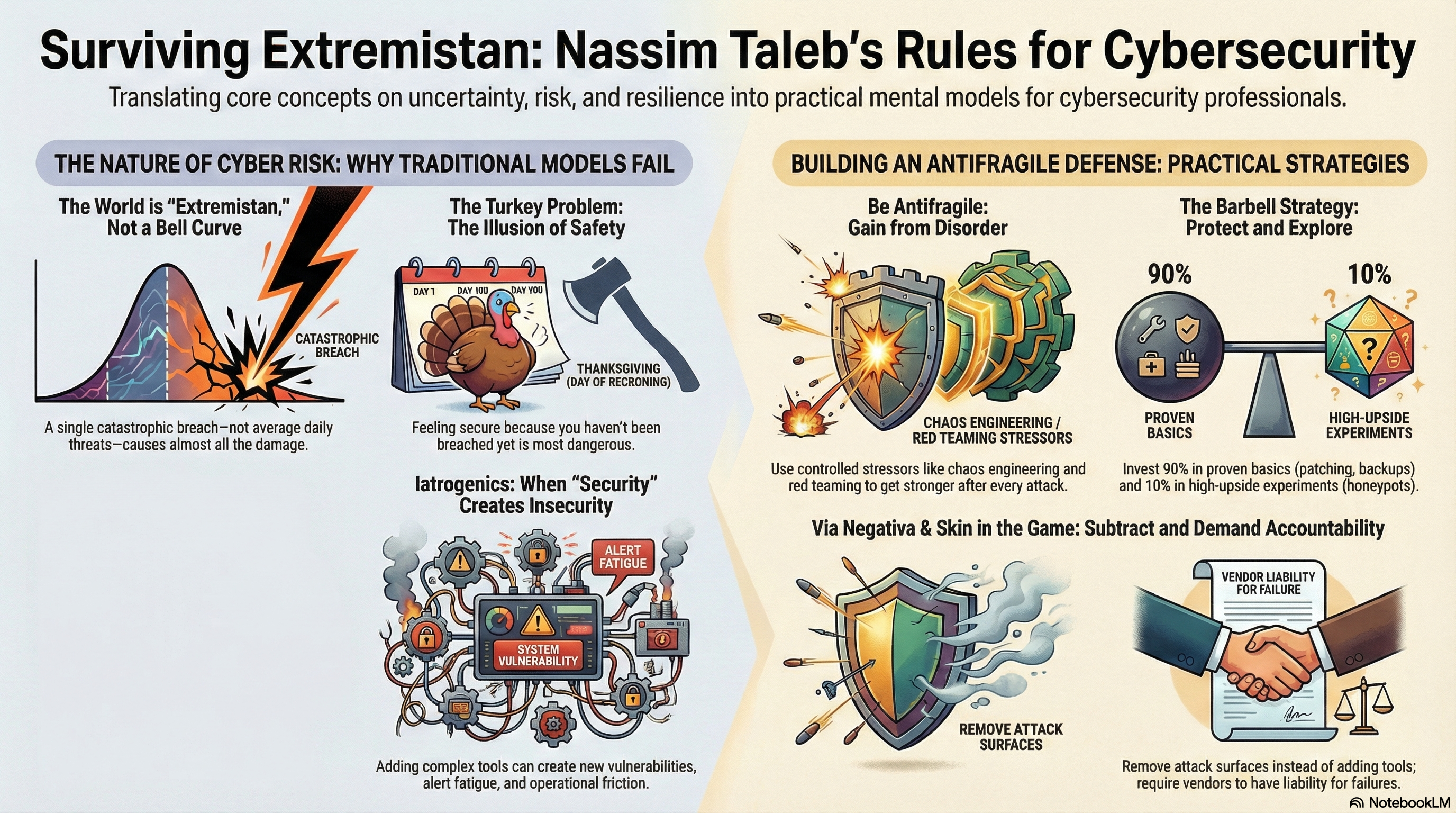
In today’s threat landscape, simply “checking the boxes” isn’t enough. Organizations invest enormous time and money to satisfy regulatory frameworks like PCI DSS, HIPAA, ISO 27001, GDPR, and NIS2—but too often they stop there. The result? A false sense of cybersecurity readiness that leaves critical vulnerabilities unaddressed and attackers unchallenged.
Compliance should be a foundation—not a finish line. Let’s unpack why checkbox compliance consistently fails modern enterprises and how forward-looking security leaders can close the gap with truly risk-based strategies.
Compliance vs. Security: Two Sides of the Same Coin?
Compliance and security are related—but they are emphatically not the same thing.
-
Compliance is about adherence to external mandates, standards, and audits.
-
Security is about reducing risk, defending against threats, and protecting data, systems, and business continuity.
Expecting compliance alone to prevent breaches is like believing that owning a fire extinguisher will stop every fire. The checklists in PCI DSS, HIPAA, or ISO standards are minimum controls designed to reduce loss—not exhaustive defenses against every attacker tactic.
“Compliance is not security.” — Security thought leaders have said this many times, and it rings true as organizations equate audit success with risk reduction.
Checkbox Security: Why It Fails
A compliance mindset often devolves into a checkbox mentality—complete documentation, filled-in forms, and green lights from auditors. But this approach contains several fundamental flaws:
1. Compliance Standards Lag Behind Evolving Threats
Most regulatory frameworks are reactive, built around known threats and past incidents. Cyber threats evolve constantly; sticking strictly to compliance means protecting against yesterday’s risks, not today’s or tomorrow’s.
2. Checklists Lack Contextual Risk Prioritization
Compliance is binary—yes/no answers. But not all controls have equal impact. A firewall might be present (box ticked), yet the organization might ignore the most actively exploited vulnerabilities like unpatched software or phishing risk.
3. Audit Success Doesn’t Equal Real-World Security
Auditors assess documentation and evidence of controls; they rarely test adversarial resilience. A compliant organization can still suffer devastating breaches because compliance assessments aren’t adversarial and don’t simulate real attacks.
Real-World Proof: Breaches Despite Compliance
Arguments against checkbox compliance sound theoretical—until you look at real breaches. Examples of organizations meeting compliance requirements yet being breached are widespread:
PCI DSS Compliance Breaches
Despite strict PCI requirements for safeguarding cardholder data, many breached organizations were technically compliant at the time of compromise. Researchers even note that no fully compliant organization examined was breach-free, and compliance fines or gaps didn’t prevent attackers from exploiting weak links in implementation.
Healthcare Data Risks Despite HIPAA
Even with stringent HIPAA requirements, healthcare breaches are rampant. Reports show thousands of HIPAA violations and data exposures annually, demonstrating that merely having compliance frameworks doesn’t stop attackers.
The Hidden Costs of Compliance-Only Security
When organizations chase compliance without aligning to deeper risk strategy, the costs go far beyond audit efforts.
1. Opportunity Cost
Security teams spend incredible hours on documentation, standard operating procedure updates, and audit response—hours that could otherwise support vulnerability remediation, threat hunting, and continuous monitoring.
2. False Sense of Security
Executives and boards often equate compliance with safety. But compliance doesn’t guarantee resilience. That false confidence can delay investments in deeper controls until it’s too late.
3. Breach Fallout
When conformity fails, consequences extend far beyond compliance fines. Reputational damage, customer churn, supply chain impacts, and board-level accountability can dwarf regulatory penalties.
Beyond Checkboxes: What Modern Security Needs
To turn compliance from checkbox security into business-aligned risk reduction, organizations should consider the following advanced practices:
1. Continuous Risk Measurement
Shift from periodic compliance assessments to continuous risk evaluation tied to real business outcomes. Tools that quantify risk exposure in financial and operational terms help prioritize investments where they matter most.
2. Threat Modeling & Adversary Emulation
Map attacker tactics relevant to your business context, then test controls against them. Frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK can help organizations think like attackers, not auditors.
3. Metrics That Measure Security Effectiveness
Move away from compliance metrics (“% of controls implemented”) to outcome metrics (“time to detect/respond to threats,” “reduction in high-risk exposures,” etc.). These demonstrate real improvements versus checkbox completion.
4. Integration of Security and Compliance
Security leaders should leverage compliance requirements as part of broader risk strategy—not substitutes. GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) platforms can tie compliance evidence to risk dashboards for a unified view.
How MicroSolved Can Help
At MicroSolved, we’ve seen these pitfalls firsthand. Organizations often approach compliance automation or external consultants expecting silver bullets—but without continuous risk measurement and business context, security controls still fall short.
MicroSolved’s approach focuses on:
-
Risk-based security program development
-
Ongoing threat modeling and adversary testing
-
Metrics and dashboards tied to business outcomes
-
Integration of compliance frameworks like PCI, HIPAA, ISO 27001 with enterprise risk strategies
If your team is struggling to move beyond checkbox compliance, we’re here to help align your cybersecurity program with real-world risk reduction—not just regulatory requirements.
➡️ Learn more about how MicroSolved can help bridge the gap between compliance and true security effectiveness.
Conclusion: Compliance Is the Floor, Not the Ceiling
Regulatory frameworks remain essential—they set the minimum expectations for protecting data and privacy. But in a world of rapidly evolving threats, compliance alone can’t be the endpoint of your cybersecurity efforts.
Checkbox security gives boards comfort, but attackers don’t check boxes—they exploit gaps.
Security leaders who integrate risk measurement, continuous validation, and business alignment into their compliance programs not only strengthen defenses—they elevate security into a source of competitive advantage.
* AI tools were used as a research assistant for this content, but human moderation and writing are also included. The included images are AI-generated.